Nvidia DLSS (Deep Learning Super Sampling) is a suite of rendering technologies that use AI-assisted techniques to help you boost your frame rate or game image quality. DLSS and DLSS 2 work by rendering frames at a lower resolution to reduce the stress placed on your GPU, before cleverly reconstructing the final image to your chosen output resolution, while DLSS 3 creates entire new frames using AI. Meanwhile, DLSS 3.5 uses similar AI-enhanced techniques to help improve ray tracing quality.
You’ll need a GPU from the GeForce RTX lineup in order to use any of the Nvidia DLSS features. Meanwhile, Nvidia DLSS 3 requires an Nvidia GeForce RTX 4000 series GPU or newer. This is one of the key differences between DLSS and AMD FidelityFX Super Resolution (FSR) and Intel XeSS, as both of these work on all brands of graphics card. Nonetheless, DLSS can be transformative for performance and image quality, allowing you to more easily enjoy the best PC games at high refresh rates.
DLSS versions
DLSS 1, DLSS 2, and DLAA
DLSS 1 (previously just known as DLSS) and DLSS 2 are both used for upscaling games from a lower render resolution to a higher output resolution. However, DLSS 1 has, to all intents and purposes, been abandoned in favor of DLSS 2. There are still five games listed on Nvidia’s DLSS compatibility list that haven’t been updated to DLSS 2 – including some bigger titles than you might expect, such as Battlefield 5 – but all the other hundreds of games use DLSS2.
There’s good reason for this because DLSS 1 was not very good. DLSS 2 improved upon it in almost every way and has since been used exclusively.
As for DLAA, this is a later addition to DLSS that takes one of the main advantages of DLSS – its ability to apply anti-aliasing to a scene via its upscaling algorithm – and apply it without any upscaling simply to improve image quality. In essence, it’s just a better version of common temporal anti-aliasing (TAA) modes so doesn’t provide a performance boost but does improve image quality.
DLSS 3
The addition of DLSS 3 is when DLSS got really confusing. Instead of just being an evolving and improving tool for upscaling games, DLSS 3 added the ability for games to generate new frames. Essentially, it’s a completely different technology to DLSS 1 and 2 but just wrapped up into a single general brand.
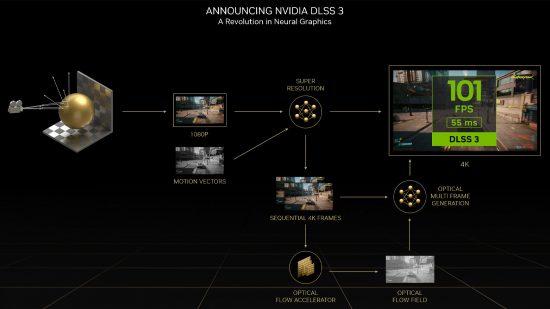
DLSS 3 frame generation, then, uses the same principle as DLSS upscaling of comparing previous frames to just-rendered ones to help create new images. But, instead of just enhancing/upscaling the latest frame of a game, DLSS 3 invents completely new whole frames. So, one frame you see will be the original game render then the next will be a wholly made up frame based on what the algorithm predicts would happen next.
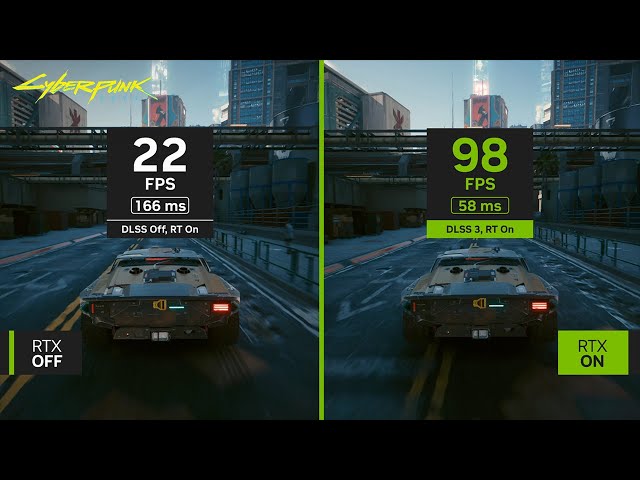
The performance increase from DLSS 3 can be huge – you can at least double your frame rate. This can make games feel smoother, which is half the battle for many games when it comes to why we want a higher frame rate. However, just as with DLSS upscaling, the downside here is that the generated frames are of course made up and as such it’s not a ideal mode to use for competitive FPS-type games where you absolutely want to know that every frame you’re seeing is a true reflection of the most up to date data.
As for the confusion mentioned above, it does kind of make sense that DLSS 3 is incorporated under the same banner as DLSS 2 because one of the key advantages of DLSS is that it inherently adds a form of anti-aliasing due to the comparison algorithm trying to make the ‘best’ looking image. As such, if you essentially didn’t have this anti-aliasing affect on the conventionally-rendered frame then did have it on the next frame because it was generated by frame generation, it would look very strange. As such, DLSS 3 always uses DLAA, even if it’s not using DLSS 2 for upscaling. But it still makes things a bit confusing.
DLSS 3.5
The final piece of the current DLSS puzzle is DLSS 3.5 ray reconstruction. This is again an essentially completely different tech to DLSS 2 and DLSS 3 but works well in conjunction so has been wrapped up in the same software suite.
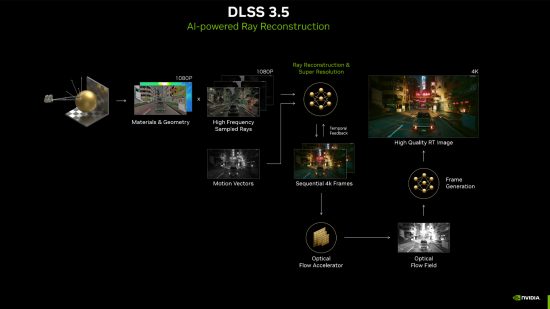
What ray reconstruction does is improve the fidelity of ray traced reflections by using AI-enhanced algorithms to better estimate how light is scattered from the reflected surface. The result is much sharper ray tracing effects with less likelihood of flickering and changes in the effect from frame to frame.
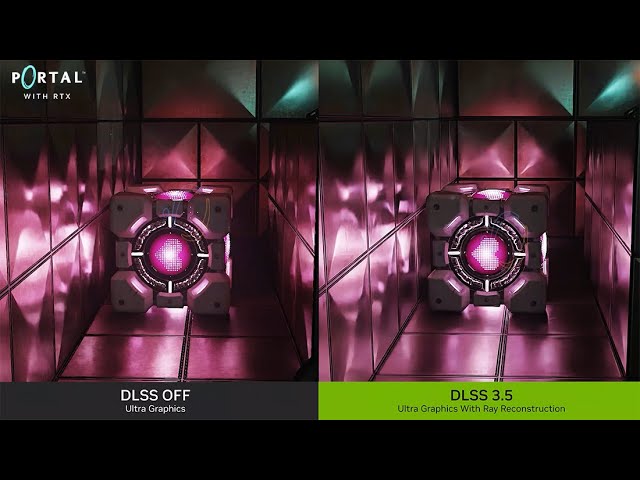
It’s a very clever feature that works very well while having relatively minimal impact on performance. If its available in a game you play, you can fairly safely turn it on without risking a plummeting frame rate.
DLSS 3.7
DLSS 3.7 is the latest update to DLSS that adds a new Quality preset (version E) that developers can use when implementing DLSS 2 modes. It’s basically a tweaked version of the algorithm that makes for “[a] slightly sharper image, improved fine detail stability, reduced ghosting and better temporal stability in general compared to DLSS 3.5.” In other words, it looks better than ever.
What is the best DLSS 2 mode?
Currently, there are up to four DLSS 2 modes to choose from: Quality, Balanced, Performance, and Ultra Performance. These mostly do what they say on the tin, either prioritising detail or putting greater emphasis on the frame rate. Looking at them from a technical standpoint, they refer to the relationship between the initially rendered image and the upscaled version:
Nvidia DLSS Quality mode
Provides a small fps boost but has the least impact on image quality.
Quality mode will use the highest initial render resolution to inform the upscaling algorithm. For instance, this means that for a 4k final image the game will render at (2,560 x 1,440) 1440p with the DLSS upscaling then stretching this to 4k. Because it starts at the highest initial resolution, it’s the most demanding of the bunch and offers the smallest performance improvement, but has the least impact on the overall quality.
This is recommended if you’re running top end hardware with a 4k monitor with very graphically rich games and you just want to squeeze a few more frames out of your game to move from, say, 50fps average to a consistent 60fps+. Or, on the other end of the scale, it’s the best mode for using with lower resolution screens on lower end hardware. That’s because the higher starting resoluition gives you the best shot at getting good image quality even on a 1080p screen (when the game is only rendering at 720p).
Nvidia DLSS Balanced mode
Has a respectable fps boost with a slight impact on quality.
You can think of Balanced as the average or ‘normal’ setting that acts as the middle-ground. It’s not quite as demanding as Quality, but it also doesn’t make the same visual sacrifices as Performance. On a 4k display, this mode will render the game at 2,227 x 1,253.
Balanced is a good mode to go for if you’re on a high resolution screen and consistently struggling to hit a decent frame rate. For instance, you might want to move from struggling to get 30-40fps to getting a consistent 60fps, or move up from 60fps to 90fps (these aren’t exact figures, but broad indicators). It’s an ideal mode for 4k screens as yoiu get a big frame rate boost while still having minimal impact on image quality. It’s more noticeable on 1440p screens, though, and is as far as you’ll generally want to go on 1080p screens.
Nvidia DLSS Performance mode
Offers the biggest fps boost, but carries more chance of blurring.
Nvidia often uses its Performance setting when showcasing just how many frames a DLSS-enabled game can push. It offers a higher frame rate but sometimes comes with a hit to its visuals, including a loss in fidelity. On a 4k screen it will render at just 1,920 x 1,080 (1080p).
Performance is very much a usable option for 4k screens. You’ll notice the drop in sharpness but image quality is still surprisingly good, generally. On 1440p screens if can look quite poor, though, and is generally quite bad-looking on 1080p screens.
Nvidia DLSS Ultra Performance mode
Gives the biggest frame rate jump, if you don’t mind blurry visuals.
Joining the roster a little later than the other options, this mode offers the lowest resolution rendering image compared to the chosen native resolution. As a result, you get the biggest leap in frame rate but this often comes with a noticeable hit to the visual quality. On a 4k screen it renders at just 1,280 x 720.
This setting is really only usable on 8k screens, which are basically non-existent. On such screens (where it’s upscaling from a 1080p output resolution), it can look ok but even on 4k screens, the 720p render resolution doesn’t look great. It’s not a viable option for lower resolution screens.
How good is DLSS 2 Performance?
DLSS performance varies depending on hardware configurations, the game you’re playing, and whether or not you’re running ray tracing, making it difficult to put a number on exactly what you can expect.
Let’s take a look at some of Nvidia’s internal numbers to get an idea of what to expect (take these with a pinch of salt):

Doom Eternal
DLSS makes ray tracing significantly more accessible, even when playing Doom Eternal at 4K resolution using max settings. Nvidia says DLSS accelerates frame rate by up to 60%, with nearly all RTX graphics cards reaching above 60fps.

Red Dead Redemption 2
Open world games are often a little more demanding than others, but Nvidia says any RTX graphics card can run Red Dead Redemption 2 at Full HD, above 60fps, on max settings with DLSS. It even lowers the barrier to entry at 4K resolution, boosting performance by up to 45%. Better yet, this extends to Red Dead Online, too.

Rainbow Six Siege
DLSS is particularly handy in competitive shooters, where each and every frame can mean the difference between a win and a loss. Quality mode is probably better if you’re running Rainbow Six Siege at 1080p or 1440p, but DLSS Performance mode lets you run 4K resolution without lowering your frame rate. You’ll see up to a 50% fps boost when running the game in UHD at max settings, and it even pushes the RTX 2060 into triple digits.

Lego Builder’s Journey
Some would consider Lego Builder’s Journey nearly unplayable at 4K resolution using max settings, as even the best graphics cards fail to achieve more than 20fps – unless you use DLSS. 60fps is still unachievable with these settings, but a potential 163% increase in frame rate gets close enough on the RTX 3080 Ti, while other GPUs firmly sit above 30fps. Those of you that prioritise frame rate will want to crank things down to 1080p with DLSS Quality on instead.

Call of Duty: Warzone
Frames matter in a game like Call of Duty: Warzone, and certainly delivers a performance hike. If you’re not willing to settle for 1080p, the green team’s AI tech can provide an FPS boost of up to 60%. Of course, if you’re playing with competitive settings, you could squeeze even more out of your gaming PC.
That said, many gamers are still rocking older graphics cards thanks to shortages, which means DLSS could help your rig keep up while it waits for an RTX 4000 series upgrade.
Remember, these are Nvidia’s internal figures and you should take them with a pinch of salt. It goes to show how DLSS can also compensate for questionable optimisation, however, as well as facilitate a smoother experience on polished games.
How does DLSS 2 work?
You may have heard the term ‘upscaling’ before, which goes some way towards visualising DLSS’s magic in action, but it’s a tad more complicated.
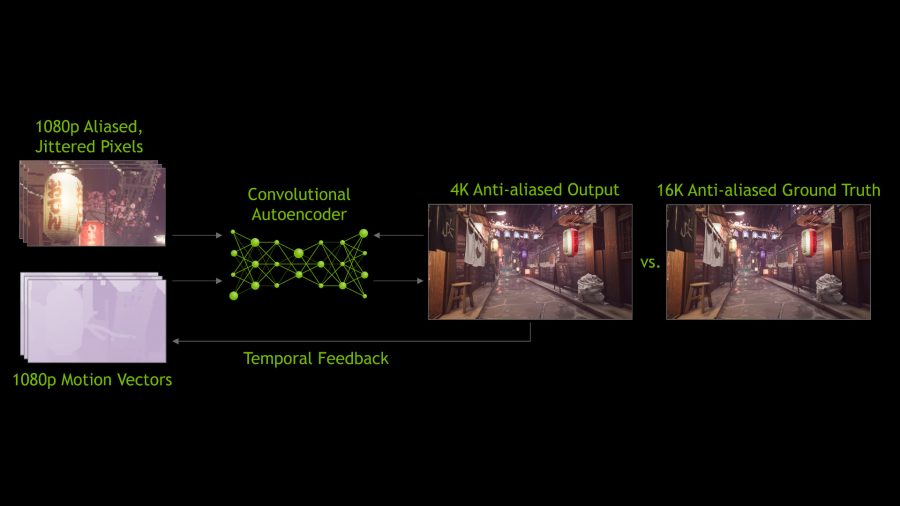
It all starts with the NGX supercomputer, where Nvidia trains its AI using machine learning. It feeds the neural network thousands of images, allowing the AI to compare ultra high-resolution stills, which are presumably 64x super sampling anti-aliased versions, with lower resolution source images that haven’t been tampered with. This allows it to reference the quality of the source image and chart a path to rebuild it into the larger version using inference.
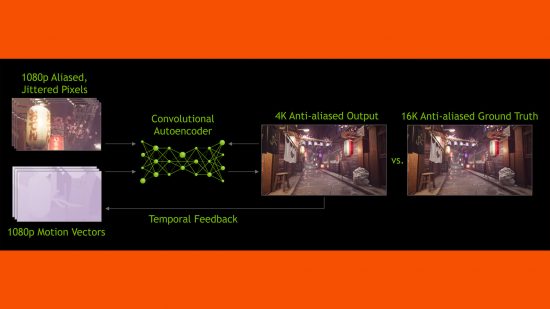
With its upscaling model trained, Nvidia can then apply this algorithm to its upscaling engine in-game. This algorithm is fed with information such as the just-rendered frame, the previously rendered frame, and motion vectors from the game that tell the algorithm how the player’s view has moved. These all allow the algorithm to calculate a prediction for what the image ‘should’ look like.
In essence, it works just like many other earlier frame-comparison techniques such as as temporal anti-aliasing (TAA). However, DLSS just works better than most such previous algorithms, producing a better overall end image that suffers less from visual glitches due to the algorithm incorrectly interpreting the change in view from one frame to the next. Also these temporal (time-based) upscaler – DLSS 2, FSR 2, and XeSS – still suffer from these glitches on occasion but in general they’re surprisingly good.

That said, the main situation where we’d recommend steering clear of DLSS or any other upscaling technique is in esports-type FPS titles. The fast movement required in these games can really mess with the algorithm and produce game outcome-affecting visual disturbances.
The first generation of DLSS (DLSS 1) required the AI to train for each and every game. DLSS 2, however, uses a general approach that allows the feature to apply AI enhancements automatically to all compatible games through Game Ready drivers. From there, RTX graphics cards use their Tensor Cores to push the improvements in real-time.
DLSS 3 builds on earlier iterations of Deep Learning to power Frame Generation. This cutting-edge upscaling technology analyzes frames to generate extra AI-created frames that the game doesn’t have to render itself, resulting in even higher frame rates DLSS 2.
What graphics cards support DLSS?
All of Nvidia’s RTX graphics cards support some form of DLSS, with all previous cards and any competitor cards from AMD or Intel not supported. For the latter you’ll need to use FSR or XeSS.
However, not all RTX cards support all features of DLSS. In particular, DLSS 3 frame generation is only available to RTX 4000 series and (presumably) later cards. Oddly, though, DLSS 3.5 ray reconstruction is available to all RTX cards. Yes, DLSS got really confusing once they went beyond it just being an upscaling tool.
The reason Nvidia gives for locking down DLSS access is that some or all of the features tap into the graphics architectures Tensor cores. These are the processors that are optimized for machine learning-type calculations – matrix multiplication and the like. However, AMD has proved with FSR that these cores aren’t essential to make an equivalent feature to DLSS, as that tech works on all graphics cards. Likewise, Intel’s XeSS is cross-platform, though it can take advantage of Intel’s own machine learning cores to get slightly better performance.
What games support DLSS?
It’s up to developers to implement DLSS, meaning not all games support it and users can’t just turn the feature/s on using the latest Nvidia driver. Instead, Nvidia has to make a concerted effort to encourage game developers to add DLSS features to their games.
Currently, there are three ways for developers to introduce DLSS into their games, including natively from within Unity, downloading the Unreal Engine plugin, or grabbing the newly available SDK. Support for DLSS is growing all the time, with new games getting the feature every month – a number we expect to grow exponentially with how accessible it now is.
You can see the hundreds of games and applications with DLSS support listed on Nvidia’s website. This resource even shows exactly which DLSS features each game includes, whether its DLSS 2, 3, 3.5, or all the above.
With Nvidia’s investment into ARM and rumours swirling about the Nintendo Switch Pro featuring a new SoC, we might eventually see DLSS appear outside of gaming PCs. For now, though, Nintendo is sticking with the current Tegra in the Switch OLED, meaning it’s only accessible on PCs rocking an RTX graphics card.
Nvidia DLSS vs AMD FSR: what’s the difference?
While Nvidia’s DLSS and AMD FSR help strike a balance between performance and resolution, both tools are fundamentally different from each other. The, while FidelityFX uses algorithms to achieve similar results.
DLSS also needs RTX GPUs with Tensor cores to work, while AMD’s FSR is compatible with a variety of graphics options. While this also limits DLSS compatibility to a specific list of games, Nvidia has a six-tap spatial upscaling alternative to FSR that works with any game, and it can be enabled within GeForce Experience.